History of Present Illness:
A 62-year-old male presents to the ED for 2-3 weeks of constant, gradually worsening, frontal headache associated with nausea and one episode of vomiting, fever up to 99.8 and mild photophobia. He denies neck stiffness, weakness or other complaints. He had a CT 3 days ago that was normal, but feels worse.
Vital Signs & Physical Exam:
Vital signs are normal except for temperature of 99.3 (not a fever, but not normal in my book). Physical exam is otherwise normal except for minimal photophobia and a positive jolt sign.
Initial Diagnostic Testing:
- Labs: CSF showed 67 WBC, most were lymphs, protein 162. Glucose and RBC count in the CSF were normal.
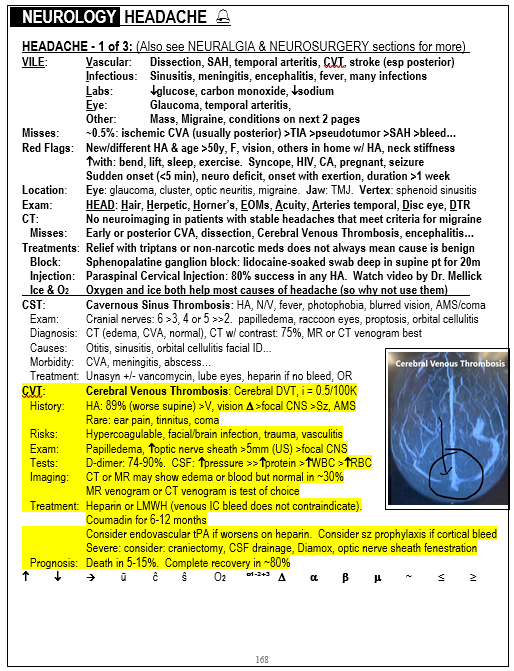
- Imaging: An MRI was done
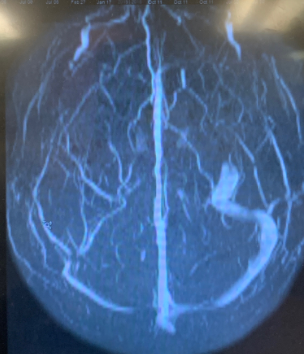
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) Meningitis
- B) Encephalitis
- C) Cerebral venous thrombosis
- D) Brain abscess
SCROLL DOWN FOR ANSWERS & 1-MINUTE CONSULT
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< ADVERTISEMENT & SPACER >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
THE EMERGENCY MEDICINE POCKETBOOK TRIFECTA

Emergency Medicine 1-Minute Consult, 5th edition
A-to-Z EM Pharmacopoeia & Antibiotic Guide, NEW 5th edition (currently printable pdf only)
8-in-1 Emergency Department Quick Reference, 5th edition
******************************************************************************
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< END SPACER >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) Meningitis – would be correct if MRI was normal
- B) Encephalitis – likely also present
- C) Cerebral venous thrombosis – CORRECT – see below
- D) Brain abscess – no but good thought given the time course of 2-3 weeks
MORE:
- What does the image show? The image is actually an MR venogram and shows a CVT. Consider brain imaging after positive LP even if not indicated before LP if the LP comes back positive and the time course is longer than a typical viral natural history, which is fever and progression in the first 5-7 days, stabilization during the second week, improvement in the third week and resolution by the end of the fourth week. Fever after the first week or worsening after the second week should raise concern for a bacterial process or other complication even if the LP looks viral, thus imaging is wise in such circumstances
- What should you do next? Initiate antibiotics, acyclovir and heparin. Consult ID and admit.
1-Minute EM Consult on the topic for this case from the Emergency Medicine 1-minute Consult Pocketbook
CLICK HERE TO LEAR MORE ABOUT THIS BOOK
CASE CONCLUSION: Although both viral culture and PCR were negative for VZV the serum VZV IgM antibody was positive signifying and acute VZV infection. The final diagnosis was VZV meningitis complicated by CVT (cerebral venous thrombosis)
CASE LESSONS:
- When the time course doesn’t fit the typical viral pattern, consider alternative or additional diagnoses.
- Meningitis or encephalitis can predispose to CVT especially when caused by HSV or VZV
- RELATED ARTICLES