History of Present Illness:
A man in his early-50’s with a h/o ESRD presents to the hospital with left shoulder pain. He denies any injury, chest symptoms or other complaints. Pain is worse with motion
Vital Signs & Physical Exam:
Vital signs are normal. Physical exam is otherwise normal except for pain with range of motion and decreased range of motion
Initial Diagnostic Testing:
- Imaging: See XR below
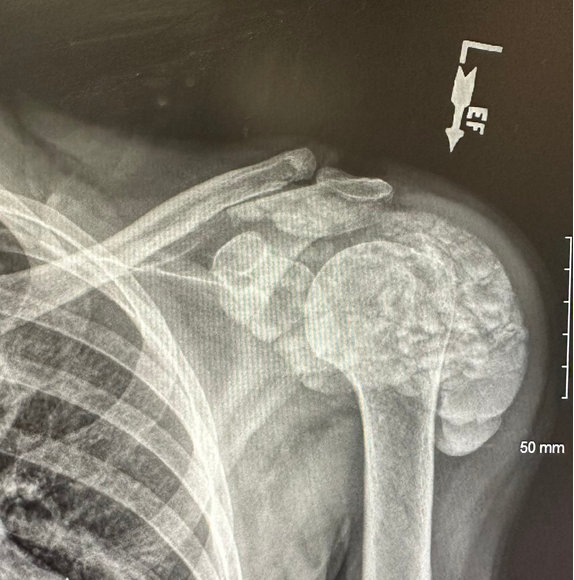
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) Calcific tendonitis
- B) Pathologic fracture with callus formation
- C) Tumoral calcinosis
- D) Osteosarcoma
SCROLL DOWN FOR ANSWERS & 1-MINUTE CONSULT
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< ADVERTISEMENT & SPACER >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
****************************************************************************
THE EMERGENCY MEDICINE POCKETBOOK TRIFECTA

Get one of our publications, all designed specifically for Emergency Care Providers:
Emergency Medicine 1-Minute Consult, 5th edition
A-to-Z EM Pharmacopoeia & Antibiotic Guide, 5th edition
8-in-1 Emergency Department Quick Reference, 5th edition
******************************************************************************
***************************************************************************
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< END SPACER >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
ANSWER: What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) Calcific tendonitis
- B) Pathologic fracture with callus formation
- C) Tumoral calcinosis – CORRECT
- D) Osteosarcoma
TUMORAL CALCINOSIS SUMMARY
- Clinical: painless swelling around joints >pain
- Types: Primary w/ high phos, Primary with normal phos, Secondary from ESRD or hyperparathyroidism
- Testing: extensive amorphous lobulated periarticular calcifications
- Treatment: Primary: Secondary: treat primary cause. Both: surgery in refractory cases
- Reference: CLICK HERE
