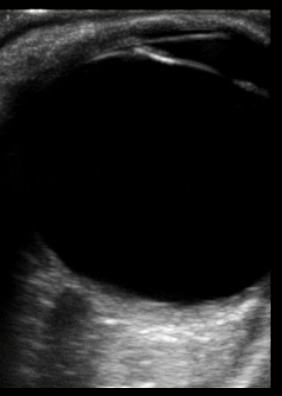
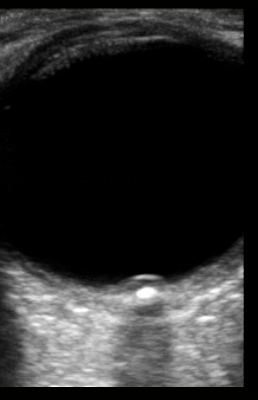
normal eye
****
This webpage contains:
-
Ocular Ultrasound
-
ENT Ultrasound
****
Ocular Ultrasound
- Probe & Positioning: Use a high frequency linear array transducer (10-13 MHz) for superficial structures such as the eye. Have the patient close the eyelid before applying ultrasound gel and have them keep their eyes closed for the entire scan. Ultrasound is contraindicated in the presence of suspected globe rupture. Applying increased pressure will not enhance your image and could theoretically worsen an eye injury. Instead, apply more ultrasound gel to improve your interface.
- Target Confirmation: Systematically obtain images of all four retinal quadrants by having the patient look up, down, left, and right during the scan. Make sure you get a clear view of the periphery where many occult findings can be missed. Scan the contra-lateral eye for a comparison view. Do not leave the probe in contact with the eyelid for more than 60 seconds at a time. Propagation of heat from the probe can theoretically coagulate the aqueous humor.
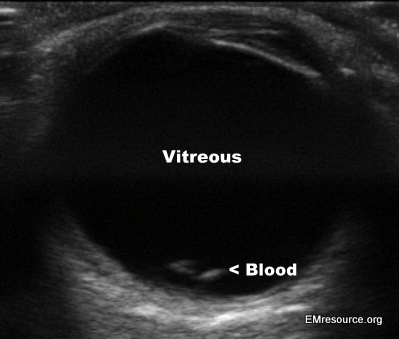
- Utility: Ocular ultrasound can be used to image the lens, vitreous, retina and optic nerve. It does not require pupillary dilatation to optimize imaging. Ultrasound is especially useful in a patient whose retina may be obscured by blood, edema, cataracts, or opacification of the cornea.
- The Retina: A retinal detachment will appear as a hyperechoic layer in front of the hyperechoic retina with a black/hypoechoic layer in between. A detached retina will often undulate with eye movement. Bear in mind that a posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) may look like a retinal detachment (RD) on ultrasound.
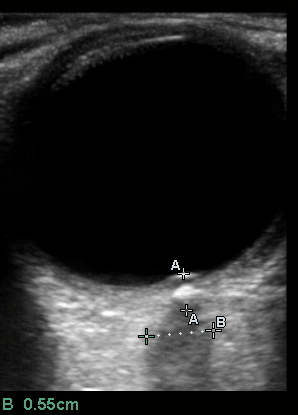
- The Optic Nerve: The optic nerve can be used to assess for elevated intracranial pressure (ICP), and can be seen immediately posterior to the globe when the ultrasound probe is oriented properly. The normal optic nerve diameter is <5 mm wide (<4.5 mm for age 1-15 years, <4 mm for age <1 year). When swollen to a larger diameter, > 5mm, it is usually an earlier sign of increased ICP than papilledema. Measurement of diameter should be taken 3 mm behind the optic disc. Measure both eyes and use the average. Sensitivity is>95%, specificity is 63% for elevated ICP.
- The Orbit: a retrobulbar hematoma may be seen as dark fluid collection surrounding the globe.
Papilledema from optic neuritis on left with normal eye on right
Measurement of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter (OSND):
ONSD = B = 0.55cm (normal < 0.5cm)
Note that “B” calipers are placed slightly further back than the recommended 0.3cm from vitreous interface (A distance) as the optic disc is bulging slightly into the vitreous and the ONSD is wider at B.
***
Severe Retinal Detachment
*
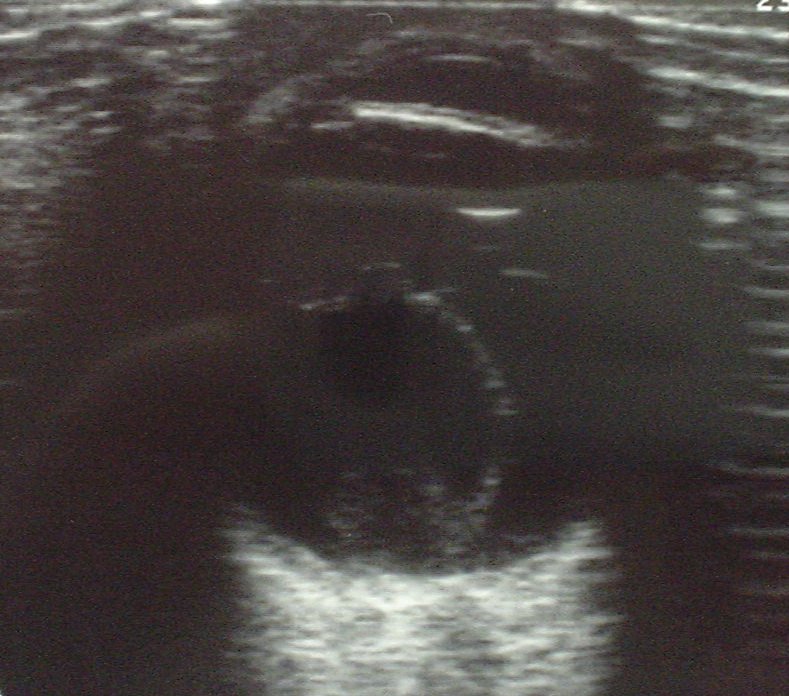
more severe retinal detachment
****
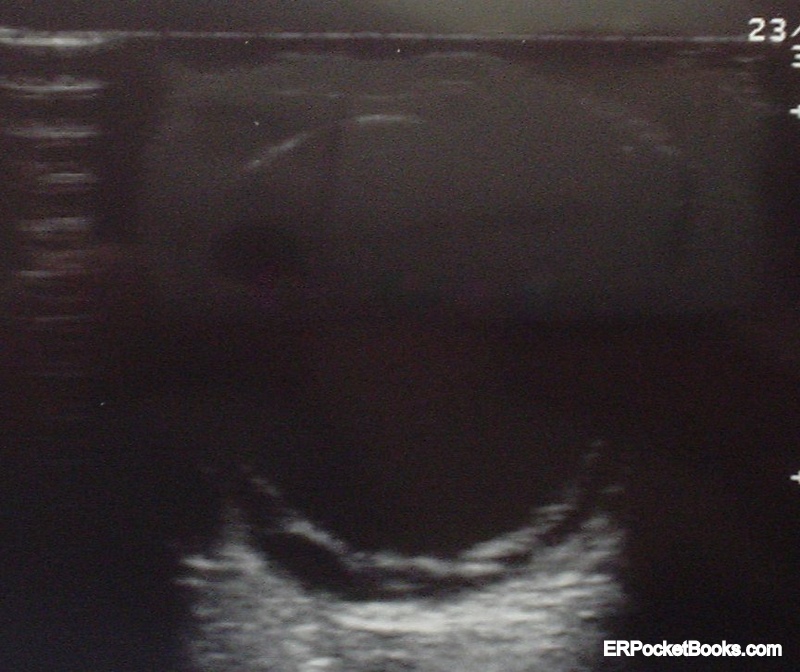
Vitreous Hemorrhage from Valsalva
****
Peritonsilar Abscess Ultrasound:
- Use the intracavitary (vaginal) probe
Epiglottitis Ultrasound
****
Do you want a pocket reference that has essential material on ED Ultrasound as well as other imaging, labs, EKG’s, procedures, risk management and more?
Then get the Tarascon Emergency Department Quick Reference Guide, 2nd edition
****
WOULD YOU LIKE TO USE ONE OF OUR IMAGES?
As long as you paste the following statement with a weblink to this site, no problem: “Image reproduced with permission, ERPocketBooks.com”
****
[wysija_form id=”1″]
****
WOULD YOU LIKE TO USE ONE OF OUR IMAGES?
As long as you paste the following statement with a weblink to this site, no problem: “Image reproduced with permission, ERPocketBooks.com”
****