History: A patient in their mid-70’s with a history of HTN and COPD is transported from home to the ER for cough, SOB and generalized weakness. She was found by medics to have a pulse ox of 89% on room air
Exam: Vitals normal other than pulse ox 89%. She is noted to be coughing, and have bibasilar rales, but no leg edema.
An ECG is done
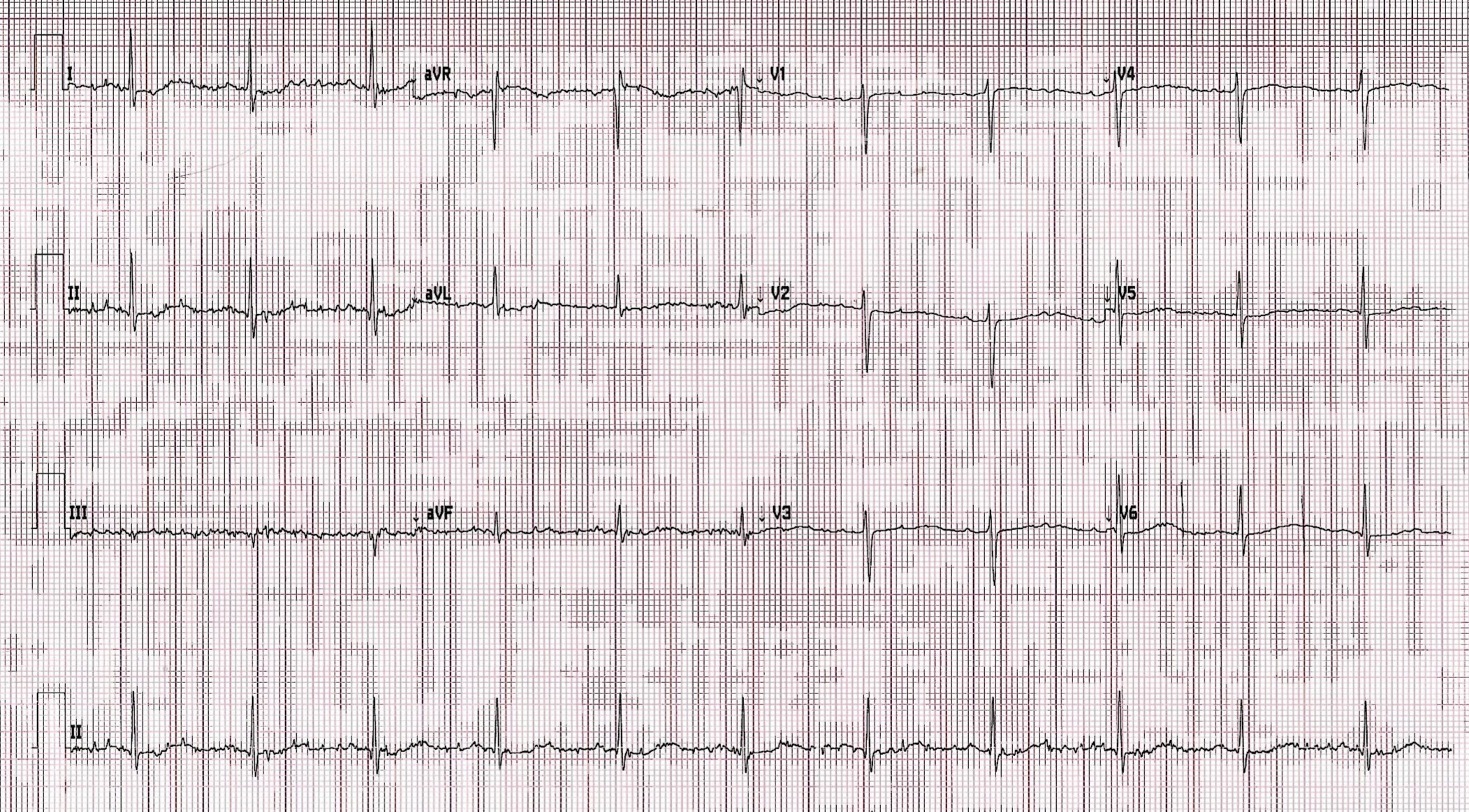
Computer Read: NSR at 67, normal intervals, nonspecific ST and T wave abnormalities
What is the most likely cause of ECG findings in this patient?
- A) Acute coronary occlusion
- B) Blood clot (PE)
- C) Cardiac tamponade
- D) Drug toxicity
- E) Electrolyte issue
Bonus Question: Your resident wants to order albuterol for her COPD. Should you agree?
SCROLL DOWN FOR THE EKG ANALYSIS & 1-MINUTE CONSULT
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< ADVERTISEMENT & SPACER >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
THE EMERGENCY MEDICINE POCKETBOOK TRIFECTA

- Emergency Medicine 1-Minute Consult, 5th edition
- A-to-Z EM Pharmacopoeia & Antibiotic Guide, NEW 5th edition
- 8-in-1 Emergency Department Quick Reference, 5th edition
******************************************************************************
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< END SPACER >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
ECG interpretation: The ECG shows very flat T waves with a long QT or U wave that the computer is missing. There are down-up T waves in lead 1. These findings are concerning for low potassium

QUIZ ANSWER:
- A) Acute coronary occlusion – not common with flat T waves
- B) Blood clot (PE) – not a good clinical fit
- C) Cardiac tamponade – no tachycardia and voltage not low
- D) Drug toxicity – good thought
- E) Electrolyte issue – CORRECT – the computer is missing a very long QT because T-waves are so flat and flat T waves blind the computer to the end of the T wave
BONUS: unless urgent albuterol indicated, which it was not here, avoid albuterol or Lasix until you get K+ level back, especially if ECG suggests low potassium
Case Outcome: K 2.5, Mg normal. Patient was on HCTZ for HTN
for the Emergency Medicine 1-Minute Consult: Click HERE and scroll to proper area.
***
